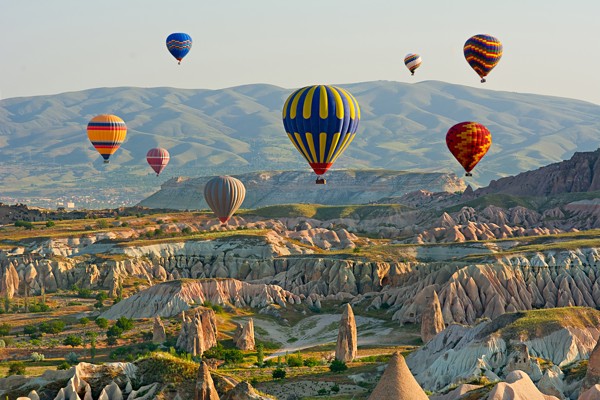
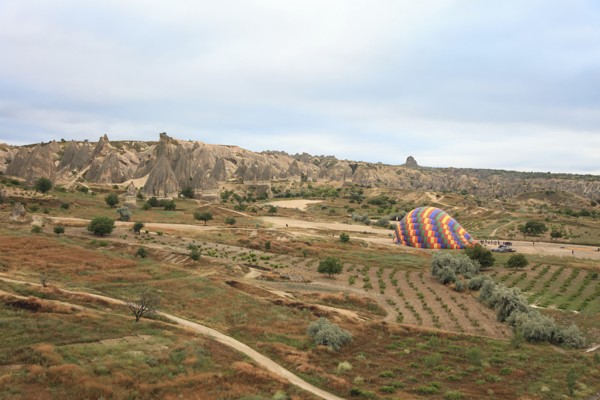
Cappadocia is a region in Turkey which lies between three provinces. It is one of Turkey’s most popular tourist destinations for its amazing topographic features and impressive views.
Did You Know?
Cappadocia is one of the best-known places in the world for hot air balloon rides. That’s because the scenic beauty in the region is stunning, and the flying conditions are excellent.
Cappadocia is a massive historical region in the central Anatolian region largely in the Nevsehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, and Niğde provinces in Turkey. It consists of a series of underground cities and villages that are scattered throughout the region.
A new place has been discovered in the Nevsehir Province by demolition workers at the time of excavation for a housing project. It consists of a network of rooms and tunnels. Numerous underground settlements like galleries, hidden churches, waterways, fountains, living rooms, kitchens, staircases and even wineries and oil presses have been discovered. Government officials say that the size and features of this new discovery could be larger than Derinkuyu, the largest excavated underground city in Cappadocia. Cappadocia is one of Turkey’s tourism capitals due to its rocky terrains, unique culture, and history.
Cappadocia Facts
Cappadocia spans an area of about 5,000 square kilometers. It is situated between three provinces namely Nevşehir, Kayseri, and Niğde in Turkey.
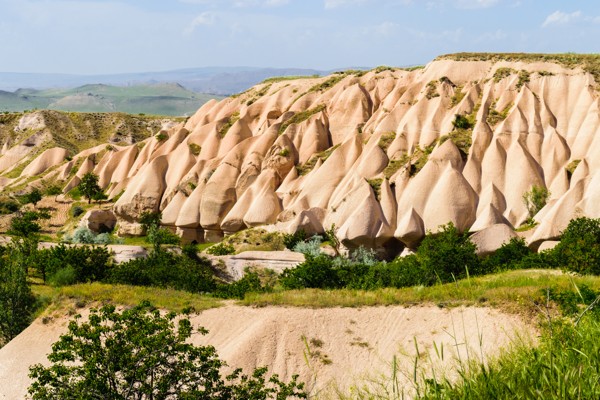
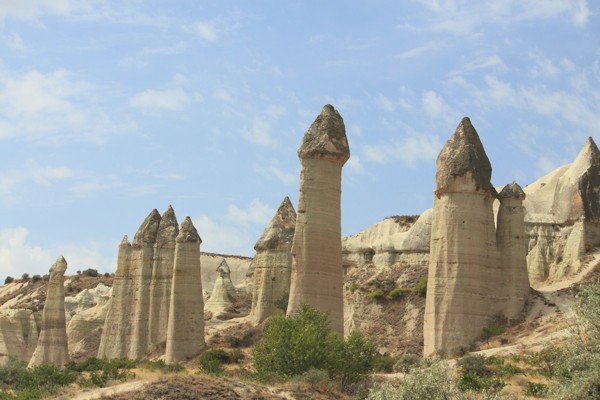
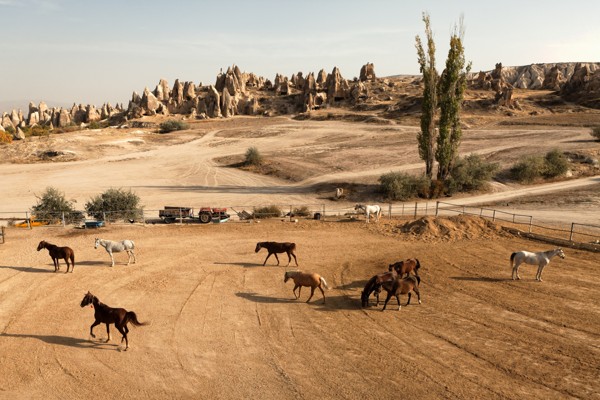
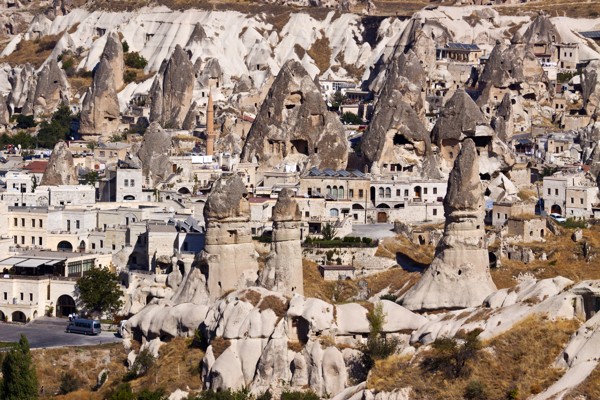
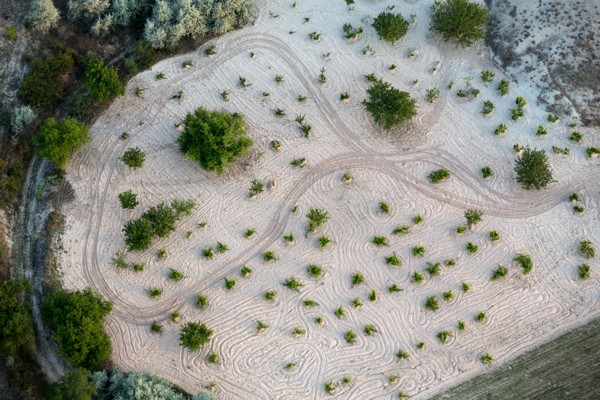
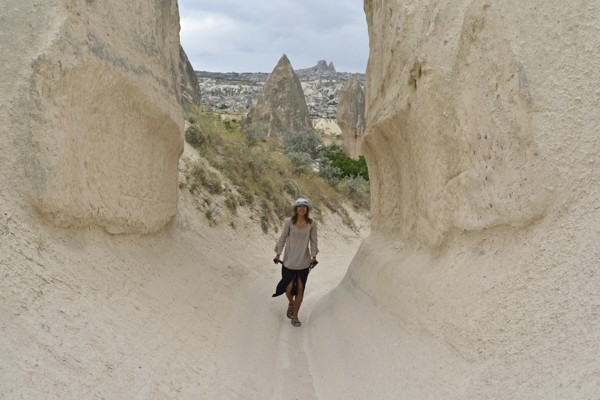
The place was buried in ash and lava due to volcanic eruptions several years ago. These geological formations or volcanic sediments were eroded by the rains and strong winds and later solidified into soft rocks known as tuffs which are several feet thick. The erosion created bizarre landscape formations such as domes, mushroom-like pillars called fairy chimneys and pinnacles that are seen today.
The volcanic rocks of Cappadocia are well-suited for the formation of fairy chimneys and pyramids due to their soft textures. The fairy chimneys vary in height and can reach as high as 40 meters.
The area is an extremely fertile land and apricots, pumpkins, melons, sugarcane, beets and chickpeas are grown here. It is also a major producer of grapes.
The Cappadocia region was once a part of the Roman empire.
It is believed that the word Cappadocia is derived from an ancient Persian word Katpatuka, which means “the land/country of beautiful horses.” In the past, Cappadocia was renowned for its horses.
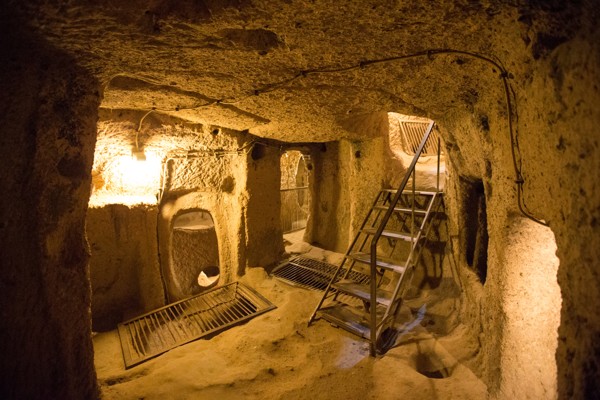
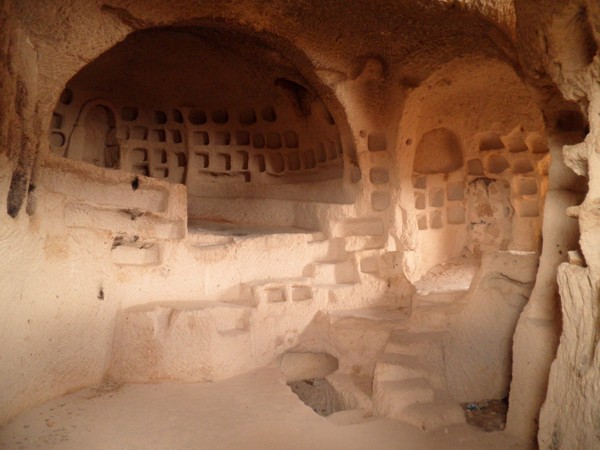
There are numerous underground cities in the region and the most popular among them are Derinkuyu and Kaymakli.
The underground dwellings in Cappadocia provided a hiding place or a refuge for the early local Christians from the Romans and later from the Muslim invaders. The Byzantine churches that were carved out of the rocks served as safe havens. The city of Derinkuyu in Cappadocia provided shelter for over 20,000 people in its caverns.
The spectacular landscape is made up of a network of human-made caves or tunnels, consisting of quarters, churches, and storehouses, which were carved out of tuffs or soft rocks. These tunnels connect the various underground settlements and are found across the entire region of Cappadocia.
The Göreme National Park and the rock sites of Cappadocia have been recognized by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in 1985 for the unusual topographic characteristics and for having more than 200 underground cities and villages.
Hiking and attending music concerts are the common activities that take place in the area.
Cappadocia was called Hatti as it was where the Hittites lived. Following the decline of the Hittite Empire, Cappadocia was governed by feudal aristocracy.
At the time when Herodotus lived, the Cappadocians occupied the areas from Mount Taurus to that surrounding Euxine (Black Sea).
Basil of Caesarea, also called Saint Basil the Great, established a monastic life in Cappadocia. He encouraged Christian monks to come and pray together in a monastery.
The region of Cappadocia in Central Turkey is known the world over, for sites like churches, houses carved in walls of valleys, and the rock formations known as fairy chimneys, among others. It is among the largest underground regions in the world.